Explore the Dangers of High Blood Pressure: Understanding Its Impact on Your Health
High blood pressure, often referred to as hypertension, is a prevalent health issue that affects millions of adults around the world. Many people remain oblivious to their high blood pressure status since it frequently shows minimal or no symptoms. This lack of awareness can be extremely dangerous, as untreated hypertension can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease and stroke. Therefore, regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial for keeping your numbers in a healthy range, enabling proactive management of your overall health.
Making small yet impactful lifestyle adjustments can greatly improve your ability to manage blood pressure effectively. Simple changes, such as adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with ensuring you get enough restorative sleep, can significantly influence your blood pressure levels. These beneficial lifestyle shifts not only enhance your cardiovascular health but also contribute to your overall vitality and well-being, allowing you to live a healthier, more energetic life.
 The Critical Role of Blood Pressure in Maintaining Your Health
The Critical Role of Blood Pressure in Maintaining Your Health
Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of your blood vessels, primarily influenced by the heart's pumping action. This vital measurement not only reflects how effectively blood circulates throughout your body but also indicates the level of resistance encountered within your arteries. Maintaining optimal blood pressure is essential for overall health, as elevated levels can lead to serious complications that impact multiple organ systems.
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and consists of two key components:
- Systolic Pressure – This is the first and higher number, representing the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats and pumps blood.
- Diastolic Pressure – This is the second and lower number, indicating the pressure in your arteries when your heart is resting between beats.
For instance, a blood pressure reading of 120/80 mmHg indicates a systolic pressure of 120 and a diastolic pressure of 80, which is generally considered normal and healthy. Monitoring these numbers regularly is crucial for early detection and management of potential health risks.
Dive Deeper into the Causes and Risks Linked to High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can arise from a multitude of factors, often associated with the narrowing of arteries that increases resistance to blood flow. This increased resistance can elevate blood pressure levels, placing undue strain on vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, brain, and eyes. If hypertension goes unmanaged, it can lead to severe health issues, particularly cardiovascular diseases, many of which can be life-threatening.
While blood pressure readings may fluctuate due to various factors, healthcare professionals categorize them according to established guidelines:
Low blood pressure – 90/60 mmHg or below
Normal blood pressure – Ranges from 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg
High blood pressure – 140/90 mmHg or higher
A reading between 120/80 mmHg and 140/90 mmHg signals a potential risk of developing hypertension in the future. However, individual blood pressure norms can vary, making it essential to consult with a healthcare provider for tailored advice and monitoring.
 Uncovering the Key Risk Factors Contributing to High Blood Pressure
Uncovering the Key Risk Factors Contributing to High Blood Pressure
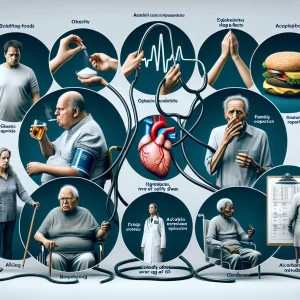
High blood pressure does not stem from a single cause; rather, it is the result of a combination of various risk factors. Some of the most prominent contributors include:
- Being overweight or obese
- Smoking
- High-sodium diet
- Family history of hypertension
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Poor sleep quality
- Lack of physical activity
- Aging, particularly over 65
- Ethnicity, such as Caribbean or African descent
Many of these risk factors can be modified through proactive lifestyle changes. In rare circumstances, high blood pressure may be linked to underlying medical conditions or specific medications, impacting roughly 1 in 20 individuals. Conditions that can contribute to hypertension include:
- Thyroid disorders
- Kidney diseases
- Diabetes
- Use of steroids
- Hormonal contraceptives
- Recreational drugs, such as cocaine
Identifying the Often Overlooked Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
One of the major challenges posed by hypertension is that it frequently presents without any noticeable symptoms, leaving many individuals unaware of their condition. In the UK, it is estimated that around 25% of adults live with undiagnosed high blood pressure. The most dependable way to evaluate your blood pressure status is through regular testing.
Blood pressure checks can be conducted at various locations, including:
- Your GP’s office or by a healthcare professional—simply ask for a blood pressure assessment.
- Many local pharmacies offer convenient blood pressure checks.
- Some workplaces provide health screenings that include blood pressure measurements.
- At home, utilizing a personal blood pressure monitor for regular self-assessments.
 Effective Strategies for Reducing Your Blood Pressure Naturally
Effective Strategies for Reducing Your Blood Pressure Naturally
Recognizing that lifestyle factors significantly influence high blood pressure, implementing effective strategies can markedly reduce your risk. Here are four essential approaches you can incorporate into your routine:
Commit to Regular Exercise for Heart Health
Incorporating consistent physical activity into your daily life is crucial for enhancing heart and blood vessel health, ultimately aiding in lowering blood pressure levels. Carrying excess weight can place additional stress on your heart, forcing it to work harder to circulate blood throughout your body. By embracing physical activity as part of your lifestyle, you can shed unnecessary weight and improve your cardiovascular fitness, both of which are instrumental in lowering blood pressure and achieving better overall health.
Embrace a Heart-Healthy Diet Rich in Nutrition
Focusing on a well-rounded diet that emphasizes whole foods—such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins—can greatly aid in lowering blood pressure levels. Since sodium is known to raise blood pressure, it is crucial to reduce your salt intake. The NHS recommends limiting salt consumption to less than 6g per day, approximately equivalent to one teaspoon. Aim to cut down on processed foods that are high in salt and instead utilize herbs and spices to flavor your meals.
Moderate Your Alcohol Intake for Better Health
Limiting both the quantity and frequency of alcohol consumption can play a significant role in effectively managing blood pressure levels. Introducing alcohol-free days into your week and spacing out your drinking occasions can positively impact your health. The NHS recommends a maximum of 14 units of alcohol per week—equivalent to 7 pints of 4% ABV beer or 7 glasses of 175ml wine—though it's vital to recognize that consistently reaching this limit is not necessary for everyone.
Prioritize Sleep for Overall Health and Well-Being
Consistently poor sleep patterns can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure. The NHS recommends aiming for 6 to 9 hours of quality sleep each night to support overall health and maintain normal blood pressure levels. Establishing a calming bedtime routine and creating an environment conducive to sleep can significantly enhance your sleep quality, which contributes to better health outcomes and helps in managing blood pressure effectively.
Presented By: Private Blood Pressure Tests
The Article Blood Pressure Test Explained: What You Need to Know Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com
The Article Blood Pressure Test: Essential Insights You Should Know First Appeared ON
: https://ad4sc.com
 Uncovering the Key Risk Factors Contributing to High Blood Pressure
Uncovering the Key Risk Factors Contributing to High Blood Pressure Effective Strategies for Reducing Your Blood Pressure Naturally
Effective Strategies for Reducing Your Blood Pressure Naturally




One response
This article touches on such an important issue! I, too, used to think high blood pressure was something that only affected older adults, but after a personal health scare in my late twenties, I’ve learned otherwise. It was eye-opening to discover how silent but dangerous hypertension can be. I started keeping track of my blood pressure regularly, and it really helped me understand how stress and my diet played significant roles in my health.